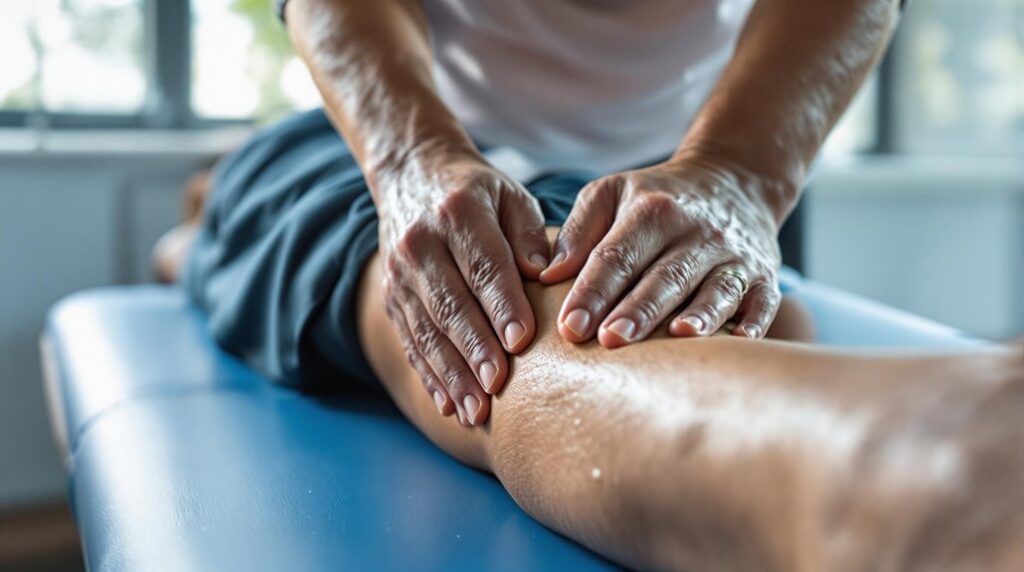
You'll prevent sports injuries effectively by incorporating tissue therapy techniques into your training routine. Focus on pre-activity massage using firm, circular motions for 30-60 seconds on major muscle groups, followed by proper warm-ups. After performance, apply ice therapy within 20 minutes and use compression garments for 2-4 hours. Regular soft tissue manipulation, including myofascial release and trigger point therapy, enhances recovery and reduces injury risk. Understanding these techniques in detail opens doors to peak athletic performance.
Understanding Common Sports Injuries and Risk Factors
Why do millions of athletes face injuries each year despite taking precautions? The answer lies in understanding both intrinsic and extrinsic risk factors that contribute to sports-related injuries. You'll find that overuse, poor technique, and inadequate recovery time are leading causes, while your individual anatomical characteristics and previous injury history can increase susceptibility.
Common injuries you're likely to encounter include sprains, strains, and stress fractures, which often result from repetitive motions and sudden directional changes. Your risk factors might include muscle imbalances, improper warm-up routines, or training errors that place excessive stress on specific body parts. It's essential that you recognize how fatigue, dehydration, and environmental conditions can affect your performance and injury potential, as these factors frequently contribute to acute and chronic injuries in athletic populations. Ankle ligaments play a crucial role in stability and injury prevention, making their integrity vital for athletes.
The Science Behind Soft Tissue Therapy
While many athletes focus primarily on strength training and conditioning, soft tissue therapy plays an essential role in injury prevention and performance enhancement. You'll find that understanding the science behind these techniques can help you make informed decisions about your recovery strategy.
| Tissue Type | Primary Function |
|---|---|
| Fascia | Connects muscles and organs |
| Tendons | Attaches muscle to bone |
| Ligaments | Connects bone to bone |
| Muscles | Enables movement and stability |
When you're receiving soft tissue therapy, the manipulation of these structures increases blood flow, reduces adhesions, and promotes cellular repair. The mechanical pressure applied during treatment stimulates mechanoreceptors, which can help decrease pain signals and improve range of motion. You'll experience both immediate and cumulative benefits as the therapy helps restore ideal tissue function and mobility. Additionally, this therapy aims to maximize movement efficiency, enhancing overall athletic performance and reducing the risk of future injuries.
Essential Pre-Activity Massage Techniques
Before engaging in any intense physical activity, you'll want to incorporate specific pre-activity massage techniques that prepare your muscles for peak performance. Start by using your palms to apply firm, circular motions to your major muscle groups, focusing on areas you'll use most during your activity. You'll need to spend 30-60 seconds on each muscle group, gradually increasing pressure to stimulate blood flow and enhance tissue pliability.
Next, incorporate cross-fiber friction techniques across your tendons and ligaments, particularly around joints you'll heavily utilize. You can perform these movements using your thumbs or knuckles, working perpendicular to the tissue fibers. Don't forget to include quick, rhythmic tapping motions to activate your muscles and nervous system, preparing them for the demands ahead. Additionally, these techniques can help enhance injury resilience by promoting better tissue health and function.
Post-Performance Recovery Methods
After completing your athletic performance, it is crucial to implement effective recovery methods that'll minimize muscle soreness and accelerate healing. You'll want to focus on techniques that promote blood circulation, reduce inflammation, and support tissue repair through targeted interventions.
- Apply ice therapy within 20 minutes post-activity to reduce swelling and inflammation in stressed muscle groups.
- Perform gentle stretching exercises, holding each position for 30-45 seconds, to maintain flexibility and prevent muscle tightness.
- Use compression garments for 2-4 hours after intense activity to improve blood flow and reduce muscle fatigue.
- Engage in light cardio cool-down activities for 10-15 minutes to facilitate lactic acid removal.
Incorporating effective recovery strategies can significantly enhance your post-performance healing process.
Remember to hydrate adequately during your recovery period and consider incorporating protein-rich foods to support muscle repair and regeneration.
Self-Massage Tools and Applications
Since self-massage techniques have become increasingly accessible, you'll find a variety of tools designed to target specific muscle groups and alleviate tension. From foam rollers and massage balls to percussion devices and compression tools, each instrument serves a unique purpose in your recovery routine.
You can use foam rollers to address large muscle groups, such as your quadriceps and back muscles, while trigger point balls work effectively on smaller areas like your feet and shoulders. Modern percussion devices offer adjustable intensity levels and interchangeable heads to customize your treatment. When you're using these tools, it's important to maintain proper form and pressure to avoid injury. You'll want to spend 30-60 seconds on each muscle group, paying special attention to areas where you experience frequent tightness or discomfort. Additionally, incorporating sports massage techniques can further enhance your recovery and performance.
Professional Treatment Protocols
While self-massage tools can provide immediate relief, professional treatment protocols offer thorough, evidence-based approaches to injury prevention and rehabilitation. You'll find that certified practitioners develop customized plans based on your specific needs, incorporating multiple therapeutic techniques.
- Physical therapists use targeted exercises and manual therapy to address biomechanical issues
- Sports medicine physicians employ diagnostic imaging to identify underlying problems
- Athletic trainers create progressive return-to-play protocols with measurable milestones
- Manual therapists integrate various soft tissue techniques, from myofascial release to joint mobilization
When you're working with professionals, they'll monitor your progress, adjust treatments as needed, and provide detailed documentation of your rehabilitation journey. You'll receive education about proper form, movement patterns, and preventive strategies that you can apply long-term to reduce injury risk.
Long-Term Injury Prevention Strategies
To maintain athletic longevity and performance, implementing thorough injury prevention strategies must become an integral part of your training routine. You'll need to focus on both active and passive prevention methods, combining proper warm-up techniques with regular tissue maintenance.
| Strategy Type | Implementation Methods |
|---|---|
| Dynamic Preparation | Mobility drills, sport-specific warm-ups |
| Strength Training | Progressive loading, stabilization exercises |
| Recovery Protocols | Active rest, compression therapy |
| Maintenance Work | Regular massage, tissue manipulation |
You should monitor your body's response to training and adjust your prevention strategies accordingly. It's crucial to maintain proper form during exercises while gradually increasing intensity to build resilience. When you're consistent with these preventive measures, you'll greatly reduce your risk of both acute and chronic injuries, allowing for sustained athletic development.